`
How to Prevent Gum Disease: Tips for Healthy Gums
Gum health should be given priority for several reasons. Gums serve as a protective barrier to prevent bacteria in the mouth from entering bloodstream. Gum health is associated with physical well-being. Home-remedies are beneficial to maintain the health of gum and keep oral cavity healthy.
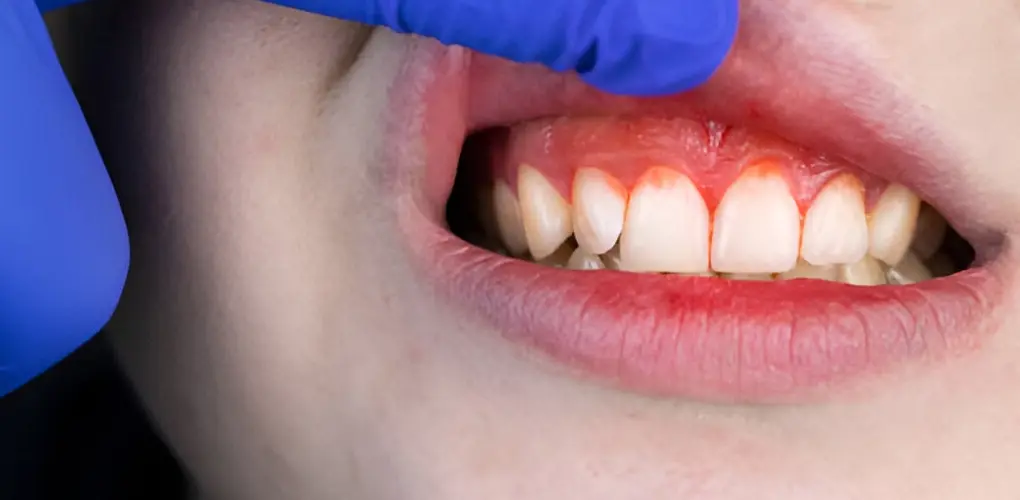
Gum disease usually presents as swollen, red, and bleeding gums during brushing and flossing. Gum disease can also create gum pockets. Gum disease originates from poor oral hygiene. Making routine dental visits is essential for spotting early signs of gum disease. Gum disease may be treated more easily the sooner issues are found.
Overview of Gum Disease
Gum disease describes the abnormality of tissues and the bones that surround and support teeth. Gum disease is generally caused by plaque build-up on tooth surfaces. Plaque contains bacteria and toxins that cause infection. If gum disease progresses, these bacteria can eventually enter the bloodstream causing systemic complications.
Gum diseases are of two types:
Gingivitis: It is a mild form of gum disease that involves gums only.
Periodontitis: It is a severe form of gum disease. It is an infection of the gums and the alveolar bone surrounding teeth.
The management of gingivitis is easy and effective. However, untreated gingivitis leads to periodontitis which causes permanent gum damage.
Causes of Gum Disease
- Poor oral hygiene
- Plaque/tartar buildup
- Unhealthy diet
- Lack of sleep
- Stress
- Medications
- Medical conditions
- Nutritional deficiency
- Heredity factors
Symptoms of Gum Disease
- Red and swollen gums
- Bleeding on brushing
- Bad breath
- Tooth sensitivity
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Difficulty in chewing
- Teeth mobility
Gum Disease Prevention
Practice good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Make sure to clean all tooth surfaces while using gentle, circular strokes. Floss every day to get rid of plaque and food between teeth and mouthwash rinse for fresh breath once daily.
A balanced diet containing fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains also helps to prevent gum diseases. Reduce sugary, acidic meals and drinks intake as they can cause gum disease and tooth decay.
Gum Disease Treatments
Early gum disease can be recognized by dentists. Dentists suggest precise treatment depending on your dental health needs. Following are the treatment options for gum diseases.
Scaling: It is the process of removing plaque/tartar from tooth surfaces and beneath the gum line.
Root planning: It is the process of smoothing root surfaces and removing existing buildup from roots.
Antibiotics: Dentists prescribe topical antibiotics to patients having severe gum diseases to control infection.
Surgery: Patients having severe gum diseases require surgery to regenerate bone and gum tissues.
Complications of Untreated Gum Disease
Gum disease can affect your gums, jawbone, and the tissues that connect your teeth to your gums. Many individuals do not notice gum disease as it is not painful. Untreated gum diseases can cause significant and long-lasting problems.
- Tooth mobility
- Gum recession
- Bone loss
Gum Disease and Overall Health
Body immunity and good oral hygiene keep the oral microorganisms in control. Bad oral hygiene leads to gum infections and increases the number of bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria can travel to other parts of the body if left untreated. These bacteria have serious health problems as:
- Endocarditis
- Pneumonia
- Birth complications
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cardiovascular disorders
Gum Disease in Children
Gingivitis is the most common type of gum disease in children. It occurs due to frequent snacking and low oral hygiene. The buildup of plaque on milk teeth is the main cause of gum diseases in children. The mild form of gum disease is not painful. So, children do not complain about it. Regular dental checkups help to prevent gum diseases in children.
Advanced Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
The most common cause of gingivitis is plaque. It can also be triggered by hormonal changes, poor hygiene habits, and smoking. Untreated gingivitis leads to periodontitis. Periodontitis can destroy the alveolar bone surrounding teeth. Periodontitis is a serious condition that can result in tooth mobility, tooth loss, and undermine the general health causing heart disease, arthritis, and many other systemic complications. It is possible to prevent periodontal disease by taking good care of your oral health.
`